The XSLT C library for GNOME
libxslt
Libxslt is the XSLT C library
developed for the GNOME project. XSLT itself is a an XML language to define
transformation for XML. Libxslt is based on libxml2 the XML C library developed for the
GNOME project. It also implements most of the EXSLT set of processor-portable extensions
functions and some of Saxon's evaluate and expressions extensions.
People can either embed the library in their application or use xsltproc
the command line processing tool. This library is free software and can be
reused in commercial applications (see the intro)
External documents:
Logo designed by Marc Liyanage.
This document describes libxslt,
the XSLT C library developed for the
GNOME project.
Here are some key points about libxslt:
- Libxslt is a C implementation
- Libxslt is based on libxml for XML parsing, tree manipulation and XPath
support
- It is written in plain C, making as few assumptions as possible, and
sticking closely to ANSI C/POSIX for easy embedding. Should works on
Linux/Unix/Windows.
- This library is released under the MIT
Licence
- Though not designed primarily with performances in mind, libxslt seems
to be a relatively fast processor.
There are some on-line resources about using libxslt:
- Check the API
documentation automatically extracted from code comments (using the
program apibuild.py, developed for libxml, together with the xsl script
'newapi.xsl' and the libxslt xsltproc program).
- Look at the mailing-list
archive.
- Of course since libxslt is based on libxml, it's a good idea to at
least read libxml description
If you need help with the XSLT language itself, here are a number of
useful resources:
Well, bugs or missing features are always possible, and I will make a
point of fixing them in a timely fashion. The best way to report a bug is to
use the GNOME bug
tracking database (make sure to use the "libxslt" module name). Before
filing a bug, check the list of existing
libxslt bugs to make sure it hasn't already been filed. I look at reports
there regularly and it's good to have a reminder when a bug is still open. Be
sure to specify that the bug is for the package libxslt.
For small problems you can try to get help on IRC, the #xml channel on
irc.gnome.org (port 6667) usually have a few person subscribed which may help
(but there is no guarantee and if a real issue is raised it should go on the
mailing-list for archival).
There is also a mailing-list xslt@gnome.org for libxslt, with an on-line archive. To subscribe
to this list, please visit the associated Web page
and follow the instructions.
Alternatively, you can just send the bug to the xslt@gnome.org list, if it's really libxslt
related I will approve it.. Please do not send me mail directly especially
for portability problem, it makes things really harder to track and in some
cases I'm not the best person to answer a given question, ask the list
instead. Do not send code, I won't debug it (but patches are
really appreciated!).
Please note that with the current amount of virus and SPAM, sending mail
to the list without being subscribed won't work. There is *far too many
bounces* (in the order of a thousand a day !) I cannot approve them manually
anymore. If your mail to the list bounced waiting for administrator approval,
it is LOST ! Repost it and fix the problem triggering the error. Also please
note that emails with
a legal warning asking to not copy or redistribute freely the information
they contain are NOT acceptable for the mailing-list,
such mail will as much as possible be discarded automatically, and are less
likely to be answered if they made it to the list, DO NOT
post to the list from an email address where such legal requirements are
automatically added, get private paying support if you can't share
information.
Check the following too before
posting:
- use the search engine to get information
related to your problem.
- make sure you are using a recent
version, and that the problem still shows up in those
- check the list
archives to see if the problem was reported already, in this case
there is probably a fix available, similarly check the registered
open bugs
- make sure you can reproduce the bug with xsltproc, a very useful thing
to do is run the transformation with -v argument and redirect the
standard error to a file, then search in this file for the transformation
logs just preceding the possible problem
- Please send the command showing the error as well as the input and
stylesheet (as an attachment)
Then send the bug with associated information to reproduce it to the xslt@gnome.org list; if it's really libxslt
related I will approve it. Please do not send mail to me directly, it makes
things really hard to track and in some cases I am not the best person to
answer a given question, ask on the list.
To be really clear about support:
- Support or help request MUST be sent to
the list or on bugzilla in case of problems, so that the Question
and Answers can be shared publicly. Failing to do so carries the implicit
message "I want free support but I don't want to share the benefits with
others" and is not welcome. I will automatically Carbon-Copy the
xslt@gnome.org mailing list for any technical reply made about libxml2 or
libxslt.
- There is no guarantee for support,
if your question remains unanswered after a week, repost it, making sure
you gave all the detail needed and the information requested.
- Failing to provide information as requested or double checking first
for prior feedback also carries the implicit message "the time of the
library maintainers is less valuable than my time" and might not be
welcome.
Of course, bugs reports with a suggested patch for fixing them will
probably be processed faster.
If you're looking for help, a quick look at the list archive may actually
provide the answer, I usually send source samples when answering libxslt
usage questions. The auto-generated documentation is
not as polished as I would like (I need to learn more about Docbook), but
it's a good starting point.
You can help the project in various ways, the best thing to do first is to
subscribe to the mailing-list as explained before, check the archives and the GNOME bug
database::
- provide patches when you find problems
- provide the diffs when you port libxslt to a new platform. They may not
be integrated in all cases but help pinpointing portability problems
and
- provide documentation fixes (either as patches to the code comments or
as HTML diffs).
- provide new documentations pieces (translations, examples, etc ...)
- Check the TODO file and try to close one of the items
- take one of the points raised in the archive or the bug database and
provide a fix. Get in touch with me
before to avoid synchronization problems and check that the suggested
fix will fit in nicely :-)
The latest versions of libxslt can be found on the xmlsoft.org server. (NOTE that
you need the libxml2,
libxml2-devel,
libxslt and libxslt-devel
packages installed to compile applications using libxslt.) Igor Zlatkovic is now the maintainer of
the Windows port, he provides
binaries. CSW provides
Solaris binaries, and
Steve Ball provides Mac Os X
binaries.
Snapshot:
Contribs:
I do accept external contributions, especially if compiling on another
platform, get in touch with me to upload the package. I will keep them in the
contrib directory
Libxslt is also available from GIT:
- Troubles compiling or linking programs using libxslt
Usually the problem comes from the fact that the compiler doesn't get
the right compilation or linking flags. There is a small shell script
xslt-config which is installed as part of libxslt usual
install process which provides those flags. Use
xslt-config --cflags
to get the compilation flags and
xslt-config --libs
to get the linker flags. Usually this is done directly from the
Makefile as:
CFLAGS=`xslt-config --cflags`
LIBS=`xslt-config --libs`
Note also that if you use the EXSLT extensions from the program then
you should prepend -lexslt to the LIBS options
- passing parameters on the xsltproc command line doesn't work
xsltproc --param test alpha foo.xsl foo.xml
the param does not get passed and ends up as ""
In a nutshell do a double escaping at the shell prompt:
xsltproc --param test "'alpha'" foo.xsl foo.xml
i.e. the string value is surrounded by " and ' then terminated by '
and ". Libxslt interpret the parameter values as XPath expressions, so
the string ->alpha<- is intepreted as the node set
matching this string. You really want ->'alpha'<- to
be passed to the processor. And to allow this you need to escape the
quotes at the shell level using ->"'alpha'"<- .
or use
xsltproc --stringparam test alpha foo.xsl foo.xml
- Is there C++ bindings ?
Yes for example xmlwrapp , see the related pages about bindings
See the git page
to get a description of the recent commits.
Those are the public releases made:
1.1.27: Sep 12 2012
- Portability:
xincludestyle wasn't protected with LIBXML_XINCLUDE_ENABLED (Michael Bonfils),
Portability fix for testThreads.c (IlyaS),
FreeBSD portability fixes (Pedro F. Giffuni),
check for gmtime - on mingw* hosts will enable date-time function (Roumen Petrov),
use only native crypto-API for mingw* hosts (Roumen Petrov),
autogen: Only check for libtoolize (Colin Walters),
minimal mingw support (Roumen Petrov),
configure: acconfig.h is deprecated since autoconf-2.50 (Stefan Kost),
Fix a small out of tree compilation issue (Hao Hu),
Fix python generator to not use deprecated xmllib (Daniel Veillard),
link python module with python library (Frederic Crozat)
- Documentation:
Tiny doc improvement (Daniel Veillard),
Various documentation fixes for docs on internals (C. M. Sperberg-McQueen)
- Bug fixes:
Report errors on variable use in key (Daniel Veillard),
The XSLT namespace string is a constant one (Daniel Veillard),
Fix handling of names in xsl:attribute (Nick Wellnhofer),
Reserved namespaces in xsl:element and xsl:attribute (Nick Wellnhofer),
Null-terminate result string of cry:rc4_decrypt (Nick Wellnhofer),
EXSLT date normalization fix (James Muscat),
Exit after compilation of invalid func:result (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix for EXSLT func:function (Nick Wellnhofer),
Rewrite EXSLT string:replace to be conformant (Nick Wellnhofer),
Avoid a heap use after free error (Chris Evans),
Fix a dictionary string usage (Chris Evans),
Output should not include extraneous newlines when indent is off (Laurence Rowe),
document('') fails to return stylesheets parsed from memory (Jason Viers),
xsltproc should return an error code if xinclude fails (Malcolm Purvis),
Forwards-compatible processing of unknown top level elements (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix system-property with unknown namespace (Nick Wellnhofer),
Hardening of code checking node types in EXSLT (Daniel Veillard),
Hardening of code checking node types in various entry point (Daniel Veillard),
Cleanup of the pattern compilation code (Daniel Veillard),
Fix default template processing on namespace nodes (Daniel Veillard),
Fix a bug in selecting XSLT elements (Daniel Veillard),
Fixed bug #616839 (Daniel Mustieles),
Fix some case of pattern parsing errors (Abhishek Arya),
preproc: fix the build (Stefan Kost),
Fix a memory leak with xsl:number (Daniel Veillard),
Fix a problem with ESXLT date:add() with January (money_seshu Dronamraju),
Fix a memory leak if compiled with Windows locale support (Daniel Veillard),
Fix generate-id() to not expose object addresses (Daniel Veillard),
Fix curlies support in literals for non-compiled AVTs (Nick Wellnhofer),
Allow whitespace in xsl:variable with select (Nick Wellnhofer),
Small fixes to locale code (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix bug 602515 (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix popping of vars in xsltCompilerNodePop (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix direct pattern matching bug (Nick Wellnhofer)
- Improvements:
Add the saxon:systemId extension (Mike Hommey),
Add an append mode to document output (Daniel Veillard),
Add new tests to EXTRA_DIST (Nick Wellnhofer),
Test for bug #680920 (Nick Wellnhofer),
fix regresson in Various "make distcheck" and other fixes (Roumen Petrov),
Various "make distcheck" and other fixes (Daniel Richard G),
Fix portability to upcoming libxml2-2.9.0 (Daniel Veillard),
Adding --system flag support to autogen.sh (Daniel Veillard),
Allow per-context override of xsltMaxDepth, introduce xsltMaxVars (Jérôme Carretero),
autogen.sh: Honor NOCONFIGURE environment variable (Colin Walters),
configure: support silent automake rules if possible (Stefan Kost),
Precompile patterns in xsl:number (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix some warnings in the refactored code (Nick Wellnhofer),
Adding new generated files (Daniel Veillard),
profiling: add callgraph report (Stefan Kost)
- Cleanups:
Big space and tabs cleanup (Daniel Veillard),
Fix authors list (Daniel Veillard),
Cleanups some of the test makefiles (Daniel Richard),
Remove .cvsignore files which are not needed anymore (Daniel Veillard),
Cleanup some misplaced spaces and tabs (Daniel Veillard),
Augment list of ignored files (Daniel Veillard),
configure: remove checks for isinf and isnan as those are not used anyway (Stefan Kost),
Point to GIT for source code and a bit of cleanup (Daniel Veillard),
Get rid of specific build setup and STATIC_BINARIES (Daniel Veillard)
1.1.26: Sep 24 2009
- Improvement:
Add xsltProcessOneNode to exported symbols for lxml (Daniel Veillard)
- Bug fixes:
Fix an idness generation problem (Daniel Veillard),
595612 Try to fix some locking problems (Daniel Veillard),
Fix a crash on misformed imported stylesheets (Daniel Veillard)
1.1.25: Sep 17 2009
- Features:
Add API versioning and various cleanups (Daniel Veillard),
xsl:sort lang support using the locale (Nick Wellnhofer and Roumen Petrov)
- Documentation:
Fix the download links for Solaris (Daniel Veillard),
Fix makefile and spec file to include doc in rpm (Daniel Veillard)
- Portability:
Make sure testThreads is linked with pthreads (Daniel Veillard),
Fix potential crash on debug of extensions Solaris (Ben Walton),
applied patch from Roumen Petrov for mingw cross compilation problems (Roumen Petrov),
patch from Richard Jones to build shared libs with MinGW cross-compiler (Richard Jones),
fix include path when compiling with MinGW (Roumen Petrov),
portability fixes ( Nick Wellnhofer and Roumen Petrov)
- Bug fixes:
Big fixes of pattern compilations (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix uses of xmlAddChild for error handling (Daniel Veillard),
Detect deep recusion on function calls (Daniel Veillard),
Avoid an error in namespace generation (Martin),
Fix importing of encoding from included stylesheets (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix problems with embedded stylesheets and namespaces (Martin),
QName parsing fix for patterns (Martin),
Crash compiling stylesheet with DTD (Martin),
Fix xsl:strip-space with namespace and wildcard (Nick Wellnhofer),
Fix a mutex deadlock on unregistered extensions (Nix),
567192 xsltproc --output option ignore --xinclude (Joachim Breitner),
Fix redundant headers in list (Daniel Veillard),
134754 Configure's --with-html-dir related fixes (Julio M. Merino Vidal),
305913 a serious problem in extensions reentrancy (Daniel Veillard),
Fix an idness issue when building the tree (Daniel Veillard),
Fixed indexing error reported by Ron Burk on the mailing list. (William M. Brack),
prevent some unchecked pointer accesses (Jake Goulding),
fix for CVE-2008-2935 libexslt RC4 encryption/decryption functions Daniel (Daniel Veillard),
avoid a quadratic behaviour when hitting duplicates (Daniel Veillard),
544829 fixed option --with-debugger (Arun Ragnavan),
541965 fixed incorrect argument popping in exsltMathAtan2Function (William M. Brack),
fix problem with string check for element-available (Ron Burk),
539741 added code to handle literal within an AVT (William M. Brack)
- Improvements:
Allow use of EXSLT outside XSLT (Martin),
Support Esperanto locale (Nick Wellnhofer),
Change how attributes are copied for id and speed (Daniel Veillard),
Add API versioning and various cleanups (Daniel Veillard),
Adding a test program to check thread reentrancy (Daniel Veillard),
big patch from finishing xsl:sort lang support (Roumen Petrov),
add xsl:sort lang support using the locale (Nick Wellnhofer)
- Cleanups:
Label xsltProcessOneNode as static (Daniel Veillard),
git setup (Daniel Veillard),
fixed typo detected by new libxml2 code (William M. Brack),
xsltExtFunctionLookup was defined but never implemented (Ralf Junker)
1.1.24: May 13 2008
- Documentation: man page fix (Vincent Lefevre).
- Bug fixes: pattern bug fix, key initialization problems, exclusion of
unknown namespaced element on top of stylesheets, python generator
syntactic cleanup (Martin)
1.1.23: Apr 8 2008
- Documentation: fix links for Cygwin DocBook setup (Philippe Bourcier),
xsltParseStylesheetDoc doc fix (Jason Viers), fix manpage default
maxdepth value
- Bug fixes: python segfault (Daniel Gryniewicz), week-in-year bug fix
(Maurice van der Pot), fix python iterator problem (William Brack),
avoid garbage collection problems on str:tokenize and str:split
and function results (William Brack and Peter Pawlowski)
superfluous re-generation of keys (William Brack), remove superfluous
code in xsltExtInitTest (Tony Graham), func:result segfault fix
(William Brack), timezone offset problem (Peter Pawlowski),
- Portability fixes: old gcrypt support fix (Brent Cowgill), Python
portability patch (Stephane Bidoul), VS 2008 fix (Rob Richard)
1.1.22: Aug 23 2007
- Bug fixes: RVT cleanup problems (William Brack), exclude-result-prefix
bug (William Brack), stylesheet compilation error handling (Rob Richards).
- Portability fixes: improve build with VS2005 (Rob Richards),
fixing build on AIX (Bjorn Wiberg), fix the security file checks on
Windows (Roland Schwarz and Rob Richards).
- Improvement: add an --encoding option to xsltproc (Drazen Kacar).
1.1.21: Jun 12 2007
- Bug fixes: out of memory allocation errors (William Brack),
namespace problem on compound predicates (William Brack),
python space/tab inconsistencies (Andreas Hanke), hook xsl:message
to per transformation error callbacks (Shaun McCance),
cached RVT problem (William Brack), XPath context maintainance
on choose (William Brack), memory leaks in the math module (William
Brack), exclude-result-prefix induced namespace problem (William
Brack)
- Build: configure setup for TRIO_REPLACE_STDIO (William Brack)
- Documentation: updated after change from CVs to SVN (William Brack)
1.1.20: Jan 17 2007
- Portability fixes: strict aliasing fix (Marcus Meissner), BSD portability
patches (Roland Illig)
- Bug fixes: Result Value Tree handling fix (William Brack), function
parameters fix (William), uninitialized variable (Kjartan Maraas),
empty text node handling (William), plugin support and test fixes (William),
fragment support fixes (William)
- Improvements: python stylesheet compare and transform context
access (Nic Ferrier), EXSLT string replace support (Joel Reed),
xsltproc better low level error handling (Mike Hommey and William)
1.1.19: Nov 29 2006
- Bug fixes: entities within attributes (William Brack), Python detection
problem (Joseph Sacco), in-scope namespace bug (Mike Hommey), Result
value tree caching bug (William Brack)
1.1.18: Oct 26 2006
- portability and build fixes: DESTDIR problem, build paths in python
shared lib, compile when libxml2 doesn't support XInclude (Gary Coady).
- bug fixes: a number of namespace related bugs (Kasimier Buchcik),
parameters bugs (Kasimier Buchcik), proximity position in predicates
of match patterns (Kasimier), exslt-node-set troubles with strings
(Kasimier), CDATA serialization, Python floats and booleans XPath
conversions, XInclude support fixes, RVT cleanup problem (William Brack
and Kasimier), attribute checking in stylesheets (Kasimier), xsltForEach
context problem (Kasimier), security check should pass full URLs (Shane
Corgatelli), security cleanup patch (Mikhail Zabaluev), some python
accessor for stylesheet were broken, memory errors when compiling
stylesheets (Mike Hommey), EXSLT current date end-of-month problem
(William Brack).
- improvements: refactoring of namespace handling, value-of impleemntation
and template internal processing (Kasimier Buchcik), new xsltproc
flag to apply Xinclude to stylesheets.
- documentation: xsltproc man pages (Daniel Leidert), tests updates
(William Brack), various typo fixes (Daniel Leidert), comments on
versions macros (Peter Breitenlohner).
1.1.17: Jun 6 2006
- portability fixes: python detection
- bug fixes: some regression tests, attribute/namespaces output (Kasimier
Buchcik), problem in mixed xsl:value-of and xsl:text uses (Kasimier)
- improvements: internal refactoring (Kasimier Buchcik), use of the XPath
object cache in libxml2-2.6.25 (Kasimier)
1.1.16: May 01 2006
- portability fixes: EXSLT date/time on Solaris and IRIX (Albert Chin),
HP-UX build (Albert Chin),
- build fixes: Python detection(Joseph Sacco), plugin configurei
(Joel Reed)
- bug fixes: pattern compilation fix(William Brack), EXSLT date/time
fix (Thomas Broyer), EXSLT function bug, potential loop on variable
eval, startup race (Christopher Palmer), debug statement left in python
(Nic Ferrier), various cleanup based on Coverity reports), error on
Out of memory condition (Charles Hardin), various namespace prefixes
fixes (Kasimier Buchcik),
- improvement: speed up sortingi, start of internals refactoring (Kasimier
Buchcik)
- documentation: man page fixes and updates (Daniel Leidert)
1.1.15: Sep 04 2005
- build fixes: Windows build cleanups and updates (Igor Zlatkovic),
remove jhbuild warnings
- bug fixes: negative number formatting (William Brack), number
formatting per mille definition (William Brack), XInclude default values
(William), text copy bugs (William), bug related to xmlXPathContext size,
reuse libxml2 memory management for text nodes, dictionary text bug,
forbid variables in match (needs libxml2-2.6.21)
- improvements: EXSLT dyn:map (Mark Vakoc),
- documentation: EXSLT date and time functions namespace in man (Jonathan
Wakely)
1.1.14: Apr 02 2005
- bug fixes: text node on stylesheet document without a dictionary
(William Brack), more checking of XSLT syntax, calling xsltInit()
multiple times, mode values interning raised by Mark Vakoc, bug in
pattern matching with ancestors, bug in patterna matching with cascading
select, xinclude and document() problem, build outside of source tree
(Mike Castle)
- improvement: added a --nodict mode to xsltproc to check problems for
docuemtns without dictionaries
1.1.13: Mar 13 2005
- build fixes: 64bits cleanup (William Brack), python 2.4 test (William),
LIBXSLT_VERSION_EXTRA on Windows (William), Windows makefiles fixes (Joel
Reed), libgcrypt-devel requires for RPM spec.
- bug fixes: exslt day-of-week-in-month (Sal Paradise), xsl:call-template
should not change the current template rule (William Brack), evaluation
of global variables (William Brack), RVT's in XPath predicates (William),
namespace URI on template names (Mark Vakoc), stat() for Windows patch
(Aleksey Gurtovoy), pattern expression fixes (William Brack), out of
memory detection misses (William), parserOptions propagation (William),
exclude-result-prefixes fix (William), // patten fix (William).
- extensions: module support (Joel Reed), dictionary based speedups
trying to get rid of xmlStrEqual as much as possible.
- documentation: added Wiki (Joel Reed)
1.1.12: Oct 29 2004
- build fixes: warnings removal (William).
- bug fixes: attribute document pointer fix (Mark Vakoc), exslt date
negative periods (William Brack), generated tree structure fixes,
namespace lookup fix, use reentrant gmtime_r (William Brack),
exslt:funtion namespace fix (William), potential NULL pointer reference
(Dennis Dams, William), force string interning on generated
documents.
- documentation: update of the second tutorial (Panagiotis Louridas), add
exslt doc in rpm packages, fix the xsltproc man page.
1.1.11: Sep 29 2004
- bug fixes: xsl:include problems (William Brack), UTF8 number pattern
(William), date-time validation (William), namespace fix (William),
various Exslt date fixes (William), error callback fixes, leak with
namespaced global variable, attempt to fix a weird problem #153137
- improvements: exslt:date-sum tests (Derek Poon)
- documentation: second tutorial by Panagiotis Lourida
1.1.10: Aug 31 2004
- build fix: NUL in c file blocking compilation on Solaris, Windows build
(Igor Zlatkovic)
- fix: key initialization problem (William Brack)
- documentation: fixed missing man page description for --path
1.1.9: Aug 22 2004
- build fixes: missing tests (William Brack), Python dependancies, Python
on 64bits boxes, --with-crypto flag (Rob Richards),
- fixes: RVT key handling (William), Python binding (William and Sitsofe
Wheeler), key and XPath troubles (William), template priority on imports
(William), str:tokenize with empty strings (William), #default namespace
alias behaviour (William), doc ordering missing for main document
(William), 64bit bug (Andreas Schwab)
- improvements: EXSLT date:sum added (Joel Reed), hook for document
loading for David Hyatt, xsltproc --nodtdattr to avoid defaulting DTD
attributes, extend xsltproc --version with CVS stamp (William).
- Documentation: web page problem reported by Oliver Stoeneberg
1.1.8: July 5 2004
- build fixes: Windows runtime options (Oliver Stoeneberg), Windows
binary package layout (Igor Zlatkovic), libgcrypt version test and link
(William)
- documentation: fix libxslt namespace name in doc (William)
- bug fixes: undefined namespace message (William Brack), search engine
(William), multiple namespace fixups (William), namespace fix for key
evaluation (William), Python memory debug bindings,
- improvements: crypto extensions for exslt (Joel Reed, William)
1.1.7: May 17 2004
- build fix: warning about localtime_r on Solaris
- bug fix: UTF8 string tokenize (William Brack), subtle memory
corruption, linefeed after comment at document level (William),
disable-output-escaping problem (William), pattern compilation in deep
imported stylesheets (William), namespace extension prefix bug,
libxslt.m4 bug (Edward Rudd), namespace lookup for attribute, namespaced
DOCTYPE name
1.1.6: Apr 18 2004
- 2 bug fixes about keys fixed one by Mark Vakoc
1.1.5: Mar 23 2004
- performance: use dictionary lookup for variables
- remove use of _private from source documents
- cleanup of "make tests" output
- bugfixes: AVT in local variables, use localtime_r to avoid thread
troubles (William), dictionary handling bug (William), limited number of
stubstitutions in AVT (William), tokenize fix for UTF-8 (William),
superfluous namespace (William), xsltproc error code on
<xsl:message> halt, OpenVMS fix, dictionary reference counting
change.
1.1.4: Feb 23 2004
- bugfixes: attributes without doc (Mariano Suárez-Alvarez), problem with
Yelp, extension problem
- display extension modules (Steve Little)
- Windows compilation patch (Mark Vadoc), Mingw (Mikhail Grushinskiy)
1.1.3: Feb 16 2004
- Rewrote the Attribute Value Template code, new XPath compilation
interfaces, dictionary reuses for XSLT with potential for serious
performance improvements.
- bug fixes: portability (William Brack), key() in node-set() results
(William), comment before doctype (William), math and node-set() problems
(William), cdata element and default namespace (William), behaviour on
unknown XSLT elements (Stefan Kost), priority of "//foo" patterns
(William), xsl:element and xsl:attribute QName check (William), comments
with -- (William), attribute namespace (William), check for ?> in PI
(William)
- Documentations: cleanup (John Fleck and William)
- Python: patch for OS-X (Gianni Ceccarelli), enums export (Stephane
bidoul)
1.1.2: Dec 24 2003
- Documentation fixes (John Fleck, William Brack), EXSLT documentation
(William Brack)
- Windows compilation fixes for MSVC and Mingw (Igor Zlatkovic)
- Bug fixes: exslt:date returning NULL strings (William Brack),
namespaces output (William Brack), key and namespace definition problem,
passing options down to the document() parser, xsl:number fixes (William
Brack)
1.1.1: Dec 10 2003
- code cleanup (William Brack)
- Windows: Makefile improvements (Igor Zlatkovic)
- documentation improvements: William Brack, libexslt man page (Jonathan
Wakely)
- param in EXSLT functions (Shaun McCance)
- XSLT debugging improvements (Mark Vakoc)
- bug fixes: number formatting (Bjorn Reese), exslt:tokenize (William
Brack), key selector parsing with | reported by Oleg Paraschenko,
xsl:element with computed namespaces (William Brack), xslt:import/include
recursion detection (William Brack), exslt:function used in keys (William
Brack), bug when CDATA_SECTION are foun in the tree (William Brack),
entities handling when using XInclude.
1.1.0: Nov 4 2003
- Removed DocBook SGML broken support
- fix xsl:key to work with PIs
- Makefile and build improvement (Graham Wilson), build cleanup (William
Brack), macro fix (Justin Fletcher), build outside of source tree (Roumen
Petrov)
- xsltproc option display fix (Alexey Efimov), --load-trace (Crutcher
Dunnavant)
- Python: never use stdout for error
- extension memory error fix (Karl Eichwalder)
- header path fixes (Steve Ball)
- added saxon:line-number() to libexslt (Brett Kail)
- Fix some tortuous template problems when using predicates (William
Brack)
- Debugger status patch (Kasimier Buchcik)
- Use new libxml2-2.6.x APIs for faster processing
- Make sure xsl:sort is empty
- Fixed a bug in default processing of attributes
- Removes the deprecated breakpoint library
- detect invalid names on templates (William Brack)
- fix exslt:document (and similar) base handling problem
1.0.33: Sep 12 2003
This is a bugfix only release
- error message missing argument (William Brack)
- mode not cascaded in template fallbacks (William Brack)
- catch redefinition of parameter/variables (William Brack)
- multiple keys with same namespace name (William Brack)
- patch for compilation using MingW on Windows (Mikhail Grushinskiy)
- header export macros for Windows (Igor Zlatkovic)
- cdata-section-elements handling of namespaced names
- compilation without libxml2 XPointer support (Mark Vadoc)
- apply-templates crash (William Brack)
- bug with imported templates (William Brack)
- imported attribute-sets merging bug (DocBook) (William Brack)
1.0.32: Aug 9 2003
- bugfixes: xsltSaveResultToFile() python binding (Chris Jaeger), EXSLT
function (William Brack), RVT for globals (William Brack), EXSLT date
(William Brack),
speed of large text output, xsl:copy with attributes, strip-space and
namespaces prefix, fix for --path xsltproc option, EXST:tokenize (Shaun
McCance), EXSLT:seconds (William Brack), sort with multiple keys (William
Brack), checking of { and } for attribute value templates (William
Brack)
- Python bindings for extension elements (Sean Treadway)
- EXSLT:split added (Shaun McCance)
- portability fixes for HP-UX/Solaris/IRIX (William Brack)
- doc cleanup
1.0.31: Jul 6 2003
1.0.30: May 4 2003
- Fixes and new APIs to handle Result Value Trees and avoid leaks
- Fixes for: EXSLT math pow() function (Charles Bozeman), global
parameter and global variables mismatch, a segfault on pattern
compilation errors, namespace copy in xsl:copy-of, python generator
problem, OpenVMS trio update, premature call to xsltFreeStackElem (Igor),
current node when templates applies to attributes
1.0.29: Apr 1 2003
- performance improvements especially for large flat documents
- bug fixes: Result Value Tree handling, XML IDs, keys(), extra namespace
declarations with xsl:elements.
- portability: python and trio fixes (Albert Chin), python on Solaris
(Ben Phillips)
1.0.28: Mar 24 2003
- fixed node() in patterns semantic.
- fixed a memory access problem in format-number()
- fixed stack overflow in recursive global variable or params
- cleaned up Result Value Tree handling, and fixed a couple of old bugs
in the process
1.0.27: Feb 24 2003
- bug fixes: spurious xmlns:nsX="" generation, serialization bug (in
libxml2), a namespace copy problem, errors in the RPM spec prereqs
- Windows path canonicalization and document cache fix (Igor)
1.0.26: Feb 10 2003
- Fixed 3 serious bugs in document() and stylesheet compilation which
could lead to a crash
1.0.25: Feb 5 2003
- Bug fix: double-free for standalone stylesheets introduced in 1.0.24, C
syntax pbm, 3 bugs reported by Eric van der Vlist
- Some XPath and XInclude related problems were actually fixed in
libxml2-2.5.2
- Documentation: emphasize taht --docbook is not for XML docs.
1.0.24: Jan 14 2003
- bug fixes: imported global varables, python bindings (Stéphane Bidoul),
EXSLT memory leak (Charles Bozeman), namespace generation on
xsl:attribute, space handling with imports (Daniel Stodden),
extension-element-prefixes (Josh Parsons), comments within xsl:text (Matt
Sergeant), superfluous xmlns generation, XInclude related bug for
numbering, EXSLT strings (Alexey Efimov), attribute-sets computation on
imports, extension module init and shutdown callbacks not called
- HP-UX portability (Alexey Efimov), Windows makefiles (Igor and Stephane
Bidoul), VMS makefile updates (Craig A. Berry)
- adds xsltGetProfileInformation() (Michael Rothwell)
- fix the API generation scripts
- API to provide the sorting routines (Richard Jinks)
- added XML description of the EXSLT API
- added ESXLT URI (un)escaping (Jörg Walter)
- Some memory leaks have been found and fixed
- document() now support fragment identifiers in URIs
1.0.23: Nov 17 2002
- Windows build cleanup (Igor)
- Unix build and RPM packaging cleanup
- Improvement of the python bindings: extension functions and activating
EXSLT
- various bug fixes: number formatting, portability for bounded string
functions, CData nodes, key(), @*[...] patterns
- Documentation improvements (John Fleck)
- added libxslt.m4 (Thomas Schraitle)
1.0.22: Oct 18 2002
- Updates on the Windows Makefiles
- Added a security module, and a related set of new options to
xsltproc
- Allowed per transformation error handler.
- Fixed a few bugs: node() semantic, URI escaping, media-type, attribute
lists
1.0.21: Sep 26 2002
- Bug fixes: match="node()", date:difference() (Igor and Charlie
Bozeman), disable-output-escaping
- Python bindings: style.saveResultToString() from Ralf Mattes
- Logos from Marc Liyanage
- Mem leak fix from Nathan Myers
- Makefile: DESTDIR fix from Christophe Merlet, AMD x86_64 (Mandrake),
Windows (Igor), Python detection
- Documentation improvements: John Fleck
1.0.20: Aug 23 2002
- Windows makefile updates (Igor) and x86-64 (Frederic Crozat)
- fixed HTML meta tag saving for Mac/IE users
- possible leak patches from Nathan Myers
- try to handle document('') as best as possible depending in the
cases
- Fixed the DocBook stylesheets handling problem
- Fixed a few XSLT reported errors
1.0.19: July 6 2002
- EXSLT: dynamic functions and date support bug fixes (Mark Vakoc)
- xsl:number fix: Richard Jinks
- xsl:format-numbers fix: Ken Neighbors
- document('') fix: bug pointed by Eric van der Vlist
- xsl:message with terminate="yes" fixes: William Brack
- xsl:sort order support added: Ken Neighbors
- a few other bug fixes, some of them requiring the latest version of
libxml2
1.0.18: May 27 2002
- a number of bug fixes: attributes, extra namespace declarations
(DocBook), xsl:include crash (Igor), documentation (Christian Cornelssen,
Charles Bozeman and Geert Kloosterman), element-available (Richard
Jinks)
- xsltproc can now list teh registered extensions thanks to Mark
Vakoc
- there is a new API to save directly to a string
xsltSaveResultToString() by Morus Walter
- specific error registration function for the python API
1.0.17: April 29 2002
- cleanup in code, XSLT debugger support and Makefiles for Windows by
Igor
- a C++ portability fix by Mark Vakoc
- EXSLT date improvement and regression tests by Charles Bozeman
- attempt to fix a bug in xsltProcessUserParamInternal
1.0.16: April 15 2002
- Bug fixes: strip-space, URL in HTML output, error when xsltproc can't
save
- portability fixes: OSF/1, IEEE on alphas, Windows, Python bindings
1.0.15: Mar 25 2002
- Bugfixes: XPath, python Makefile, recursive attribute sets, @foo[..]
templates
- Debug of memory alocation with valgind
- serious profiling leading to significant improvement for DocBook
processing
- revamp of the Windows build
1.0.14: Mar 18 2002
- Improvement in the XPath engine (libxml2-2.4.18)
- Nasty bug fix related to exslt:node-set
- Fixed the python Makefiles, cleanup of doc comments, Windows
portability fixes
1.0.13: Mar 8 2002
- a number of bug fixes including "namespace node have no parents"
- Improvement of the Python bindings
- Charles Bozeman provided fixes and regression tests for exslt date
functions.
1.0.12: Feb 11 2002
- Fixed the makefiles especially the python module ones
- half a dozen bugs fixes including 2 old ones
1.0.11: Feb 8 2002
- Change of Licence to the MIT
Licence
- Added a beta version of the Python bindings, including support to
extend the engine with functions written in Python
- A number of bug fixes
- Charlie Bozeman provided more EXSLT functions
- Portability fixes
1.0.10: Jan 14 2002
- Windows fixes for Win32 from Igor
- Fixed the Solaris compilation trouble (Albert)
- Documentation changes and updates: John Fleck
- Added a stringparam option to avoid escaping hell at the shell
level
- A few bug fixes
1.0.9: Dec 7 2001
- Makefile patches from Peter Williams
- attempt to fix the compilation problem associated to prelinking
- obsoleted libxsltbreakpoint now deprecated and frozen to 1.0.8 API
- xsltproc return codes are now significant, John Fleck updated the
documentation
- patch to allow as much as 40 steps in patterns (Marc Tardif), should be
made dynamic really
- fixed a bug raised by Nik Clayton when using doctypes with HTML
output
- patches from Keith Isdale to interface with xsltdebugger
1.0.8: Nov 26 2001
- fixed an annoying header problem, removed a few bugs and some code
cleanup
- patches for Windows and update of Windows Makefiles by Igor
- OpenVMS port instructions from John A Fotheringham
- fixed some Makefiles annoyance and libraries prelinking
information
1.0.7: Nov 10 2001
- remove a compilation problem with LIBXSLT_PUBLIC
- Finishing the integration steps for Keith Isdale debugger
- fixes the handling of indent="no" on HTML output
- fixes on the configure script and RPM spec file
1.0.6: Oct 30 2001
- bug fixes on number formatting (Thomas), date/time functions (Bruce
Miller)
- update of the Windows Makefiles (Igor)
- fixed DOCTYPE generation rules for HTML output (me)
1.0.5: Oct 10 2001
- some portability fixes, including Windows makefile updates from
Igor
- fixed a dozen bugs on XSLT and EXSLT (me and Thomas Broyer)
- support for Saxon's evaluate and expressions extensions added (initial
contribution from Darren Graves)
- better handling of XPath evaluation errors
1.0.4: Sep 12 2001
- Documentation updates from John fleck
- bug fixes (DocBook FO generation should be fixed) and portability
improvements
- Thomas Broyer improved the existing EXSLT support and added String,
Time and Date core functions support
1.0.3: Aug 23 2001
- XML Catalog support see the doc
- New NaN/Infinity floating point code
- A few bug fixes
1.0.2: Aug 15 2001
- lot of bug fixes, increased the testsuite
- a large chunk of EXSLT is implemented
- improvements on the extension framework
- documentation improvements
- Windows MSC projects files should be up-to-date
- handle attributes inherited from the DTD by default
1.0.1: July 24 2001
- initial EXSLT framework
- better error reporting
- fixed the profiler on Windows
- bug fixes
1.0.0: July 10 2001
- a lot of cleanup, a lot of regression tests added or fixed
- added a documentation for writing
extensions
- fixed some variable evaluation problems (with William)
- added profiling of stylesheet execution accessible as the xsltproc
--profile option
- fixed element-available() and the implementation of the various
chunking methods present, Norm Walsh provided a lot of feedback
- exclude-result-prefixes and namespaces output should now work as
expected
- added support of embedded stylesheet as described in section 2.7 of the
spec
0.14.0: July 5 2001
- lot of bug fixes, and code cleanup
- completion of the little XSLT-1.0 features left unimplemented
- Added and implemented the extension API suggested by Thomas Broyer
- the Windows MSC environment should be complete
- tested and optimized with a really large document (DocBook Definitive
Guide) libxml/libxslt should really be faster on serious workloads
0.13.0: June 26 2001
- lots of cleanups
- fixed a C++ compilation problem
- couple of fixes to xsltSaveTo()
- try to fix Docbook-xslt-1.4 and chunking, updated the regression test
with them
- fixed pattern compilation and priorities problems
- Patches for Windows and MSC project mostly contributed by Yon Derek
- update to the Tutorial by John Fleck
- William fixed bugs in templates and for-each functions
- added a new interface xsltRunStylesheet() for a more flexible output
(incomplete), added -o option to xsltproc
0.12.0: June 18 2001
- fixed a dozen of bugs reported
- HTML generation should be quite better (requires libxml-2.3.11 upgrade
too)
- William fixed some problems with document()
- Fix namespace nodes selection and copy (requires libxml-2.3.11 upgrade
too)
- John Fleck added a
tutorial
- Fixes for namespace handling when evaluating variables
- XInclude global flag added to process XInclude on document() if
requested
- made xsltproc --version more detailed
0.11.0: June 1 2001
Mostly a bug fix release.
- integration of catalogs from xsltproc
- added --version to xsltproc for bug reporting
- fixed errors when handling ID in external parsed entities
- document() should hopefully work correctly but ...
- fixed bug with PI and comments processing
- William fixed the XPath string functions when using unicode
0.10.0: May 19 2001
- cleanups to make stylesheet read-only (not 100% complete)
- fixed URI resolution in document()
- force all XPath expression to be compiled at stylesheet parsing time,
even if unused ...
- Fixed HTML default output detection
- Fixed double attribute generation #54446
- Fixed {{ handling in attributes #54451
- More tests and speedups for DocBook document transformations
- Fixed a really bad race like bug in xsltCopyTreeList()
- added a documentation on the libxslt internals
- William Brack and Bjorn Reese improved format-number()
- Fixed multiple sort, it should really work now
- added a --docbook option for SGML DocBook input (hackish)
- a number of other bug fixes and regression test added as people were
submitting them
0.9.0: May 3 2001
- lot of various bugfixes, extended the regression suite
- xsltproc should work with multiple params
- added an option to use xsltproc with HTML input
- improved the stylesheet compilation, processing of complex stylesheets
should be faster
- using the same stylesheet for concurrent processing on multithreaded
programs should work now
- fixed another batch of namespace handling problems
- Implemented multiple level of sorting
0.8.0: Apr 22 2001
- fixed ansidecl.h problem
- fixed unparsed-entity-uri() and generate-id()
- sort semantic fixes and priority prob from William M. Brack
- fixed namespace handling problems in XPath expression computations
(requires libxml-2.3.7)
- fixes to current() and key()
- other, smaller fixes, lots of testing with N Walsh DocBook HTML
stylesheets
0.7.0: Apr 10 2001
- cleanup using stricter compiler flags
- command line parameter passing
- fix to xsltApplyTemplates from William M. Brack
- added the XSLTMark in the regression tests as well as document()
0.6.0: Mar 22 2001
- another beta
- requires 2.3.5, which provide XPath expression compilation support
- document() extension should function properly
- fixed a number or reported bugs
0.5.0: Mar 10 2001
- fifth beta
- some optimization work, for the moment 2 XSLT transform cannot use the
same stylesheet at the same time (to be fixed)
- fixed problems with handling of tree results
- fixed a reported strip-spaces problem
- added more reported/fixed bugs to the test suite
- incorporated William M. Brack fix for imports and global variables as
well as patch for with-param support in apply-templates
- a bug fix on for-each
0.4.0: Mar 1 2001
- fourth beta test, released at the same time of libxml2-2.3.3
- bug fixes
- some optimization
- started implement extension support, not finished
- implemented but not tested multiple file output
0.3.0: Feb 24 2001
- third beta test, released at the same time of libxml2-2.3.2
- lot of bug fixes
- some optimization
- added DocBook XSL based testsuite
0.2.0: Feb 15 2001
- second beta version, released at the same time as libxml2-2.3.1
- getting close to feature completion, lot of bug fixes, some in the HTML
and XPath support of libxml
- start becoming usable for real work. This version can now regenerate
the XML 2e HTML from the original XML sources and the associated
stylesheets (in section I of the XML
REC)
- Still misses extension element/function/prefixes support. Support of
key() and document() is not complete
0.1.0: Feb 8 2001
- first beta version, released at the same time as libxml2-2.3.0
- lots of bug fixes, first "testing" version, but incomplete
0.0.1: Jan 25 2001
- first alpha version released at the same time as libxml2-2.2.12
- Framework in place, should work on simple examples, but far from being
feature complete
This program is the simplest way to use libxslt: from the command line. It
is also used for doing the regression tests of the library.
It takes as first argument the path or URL to an XSLT stylesheet, the next
arguments are filenames or URIs of the inputs to be processed. The output of
the processing is redirected on the standard output. There is actually a few
more options available:
orchis:~ -> xsltproc
Usage: xsltproc [options] stylesheet file [file ...]
Options:
--version or -V: show the version of libxml and libxslt used
--verbose or -v: show logs of what's happening
--output file or -o file: save to a given file
--timing: display the time used
--repeat: run the transformation 20 times
--debug: dump the tree of the result instead
--novalid: skip the DTD loading phase
--noout: do not dump the result
--maxdepth val : increase the maximum depth
--html: the input document is(are) an HTML file(s)
--docbook: the input document is SGML docbook
--param name value : pass a (parameter,value) pair
--nonet refuse to fetch DTDs or entities over network
--warnnet warn against fetching over the network
--catalogs : use the catalogs from $SGML_CATALOG_FILES
--xinclude : do XInclude processing on document input
--profile or --norman : dump profiling information
orchis:~ ->

DocBook is an
XML/SGML vocabulary particularly well suited to books and papers about
computer hardware and software.
xsltproc and libxslt are not specifically dependant on DocBook, but since
a lot of people use xsltproc and libxml2 for DocBook formatting, here are a
few pointers and information which may be helpful:
Do not use the --docbook option of xsltproc to process XML DocBook
documents, this option is only intended to provide some (limited) support of
the SGML version of DocBook.
Points which are not DocBook specific but still worth mentionning
again:
- if you think DocBook processing time is too slow, make sure you have
XML Catalogs pointing to a local installation of the DTD of DocBook.
Check the XML Catalog page
to understand more on this subject.
- before processing a new document, use the command
xmllint --valid --noout path_to_document
to make sure that your input is valid DocBook. And fixes the errors
before processing further. Note that XSLT processing may work correctly
with some forms of validity errors left, but in general it can give
troubles on output.
Okay this section is clearly incomplete. But integrating libxslt into your
application should be relatively easy. First check the few steps described
below, then for more detailed information, look at the generated pages for the API and the source
of libxslt/xsltproc.c and the tutorial.
Basically doing an XSLT transformation can be done in a few steps:
- configure the parser for XSLT:
xmlSubstituteEntitiesDefault(1);
xmlLoadExtDtdDefaultValue = 1;
- parse the stylesheet with xsltParseStylesheetFile()
- parse the document with xmlParseFile()
- apply the stylesheet using xsltApplyStylesheet()
- save the result using xsltSaveResultToFile() if needed set
xmlIndentTreeOutput to 1
Steps 2,3, and 5 will probably need to be changed depending on you
processing needs and environment for example if reading/saving from/to
memory, or if you want to apply XInclude processing to the stylesheet or
input documents.
There is a number of language bindings and wrappers available for libxml2,
the list below is not exhaustive. Please contact the xml-bindings@gnome.org
(archives) in
order to get updates to this list or to discuss the specific topic of libxml2
or libxslt wrappers or bindings:
The libxslt Python module depends on the libxml2 Python module.
The distribution includes a set of Python bindings, which are guaranteed to
be maintained as part of the library in the future, though the Python
interface have not yet reached the completeness of the C API.
Stéphane Bidoul
maintains a Windows port
of the Python bindings.
Note to people interested in building bindings, the API is formalized as
an XML API description file which allows to
automate a large part of the Python bindings, this includes function
descriptions, enums, structures, typedefs, etc... The Python script used to
build the bindings is python/generator.py in the source distribution.
To install the Python bindings there are 2 options:
- If you use an RPM based distribution, simply install the libxml2-python
RPM and the libxslt-python
RPM.
- Otherwise use the libxml2-python
module distribution corresponding to your installed version of
libxml2 and libxslt. Note that to install it you will need both libxml2
and libxslt installed and run "python setup.py build install" in the
module tree.
The distribution includes a set of examples and regression tests for the
python bindings in the python/tests directory. Here are some
excepts from those tests:
basic.py:
This is a basic test of XSLT interfaces: loading a stylesheet and a
document, transforming the document and saving the result.
import libxml2
import libxslt
styledoc = libxml2.parseFile("test.xsl")
style = libxslt.parseStylesheetDoc(styledoc)
doc = libxml2.parseFile("test.xml")
result = style.applyStylesheet(doc, None)
style.saveResultToFilename("foo", result, 0)
style.freeStylesheet()
doc.freeDoc()
result.freeDoc()
The Python module is called libxslt, you will also need the libxml2 module
for the operations on XML trees. Let's have a look at the objects manipulated
in that example and how is the processing done:
styledoc : is a libxml2 document tree. It is obtained by
parsing the XML file "test.xsl" containing the stylesheet.style : this is a precompiled stylesheet ready to be used
by the following transformations (note the plural form, multiple
transformations can resuse the same stylesheet).doc : this is the document to apply the transformation to.
In this case it is simply generated by parsing it from a file but any
other processing is possible as long as one get a libxml2 Doc. Note that
HTML tree are suitable for XSLT processing in libxslt. This is actually
how this page is generated !result : this is a document generated by applying the
stylesheet to the document. Note that some of the stylesheet information
may be related to the serialization of that document and as in this
example a specific saveResultToFilename() method of the stylesheet should
be used to save it to a file (in that case to "foo").
Also note the need to explicitely deallocate documents with freeDoc()
except for the stylesheet document which is freed when its compiled form is
garbage collected.
extfunc.py:
This one is a far more complex test. It shows how to modify the behaviour
of an XSLT transformation by passing parameters and how to extend the XSLT
engine with functions defined in python:
import libxml2
import libxslt
import string
nodeName = None
def f(ctx, str):
global nodeName
#
# Small check to verify the context is correcly accessed
#
try:
pctxt = libxslt.xpathParserContext(_obj=ctx)
ctxt = pctxt.context()
tctxt = ctxt.transformContext()
nodeName = tctxt.insertNode().name
except:
pass
return string.upper(str)
libxslt.registerExtModuleFunction("foo", "http://example.com/foo", f)
This code defines and register an extension function. Note that the
function can be bound to any name (foo) and how the binding is also
associated to a namespace name "http://example.com/foo". From an XSLT point
of view the function just returns an upper case version of the string passed
as a parameter. But the first part of the function also read some contextual
information from the current XSLT processing environement, in that case it
looks for the current insertion node in the resulting output (either the
resulting document or the Result Value Tree being generated), and saves it to
a global variable for checking that the access actually worked.
For more information on the xpathParserContext and transformContext
objects check the libray internals description.
The pctxt is actually an object from a class derived from the
libxml2.xpathParserContext() with just a couple more properties including the
possibility to look up the XSLT transformation context from the XPath
context.
styledoc = libxml2.parseDoc("""
<xsl:stylesheet version='1.0'
xmlns:xsl='http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform'
xmlns:foo='http://example.com/foo'
xsl:exclude-result-prefixes='foo'>
<xsl:param name='bar'>failure</xsl:param>
<xsl:template match='/'>
<article><xsl:value-of select='foo:foo($bar)'/></article>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
""")
Here is a simple example of how to read an XML document from a python
string with libxml2. Note how this stylesheet:
- Uses a global parameter
bar
- Reference the extension function f
- how the Namespace name "http://example.com/foo" has to be bound to a
prefix
- how that prefix is excluded from the output
- how the function is called from the select
style = libxslt.parseStylesheetDoc(styledoc)
doc = libxml2.parseDoc("<doc/>")
result = style.applyStylesheet(doc, { "bar": "'success'" })
style.freeStylesheet()
doc.freeDoc()
that part is identical, to the basic example except that the
transformation is passed a dictionary of parameters. Note that the string
passed "success" had to be quoted, otherwise it is interpreted as an XPath
query for the childs of root named "success".
root = result.children
if root.name != "article":
print "Unexpected root node name"
sys.exit(1)
if root.content != "SUCCESS":
print "Unexpected root node content, extension function failed"
sys.exit(1)
if nodeName != 'article':
print "The function callback failed to access its context"
sys.exit(1)
result.freeDoc()
That part just verifies that the transformation worked, that the parameter
got properly passed to the engine, that the function f() got called and that
it properly accessed the context to find the name of the insertion node.
pyxsltproc.py:
this module is a bit too long to be described there but it is basically a
rewrite of the xsltproc command line interface of libxslt in Python. It
provides nearly all the functionalities of xsltproc and can be used as a base
module to write Python customized XSLT processors. One of the thing to notice
are:
libxml2.lineNumbersDefault(1)
libxml2.substituteEntitiesDefault(1)
those two calls in the main() function are needed to force the libxml2
processor to generate DOM trees compliant with the XPath data model.
Table of contents
This document describes the processing of libxslt, the XSLT C library developed for the GNOME project.
Note: this documentation is by definition incomplete and I am not good at
spelling, grammar, so patches and suggestions are really welcome.
XSLT is a transformation language. It takes an input document and a
stylesheet document and generates an output document:
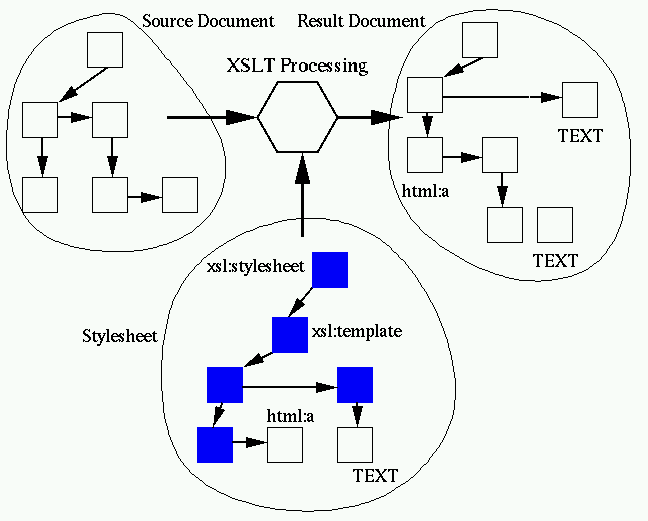
Libxslt is written in C. It relies on libxml, the XML C library for GNOME, for
the following operations:
- parsing files
- building the in-memory DOM structure associated with the documents
handled
- the XPath implementation
- serializing back the result document to XML and HTML. (Text is handled
directly.)
Libxslt is not very specialized. It is built under the assumption that all
nodes from the source and output document can fit in the virtual memory of
the system. There is a big trade-off there. It is fine for reasonably sized
documents but may not be suitable for large sets of data. The gain is that it
can be used in a relatively versatile way. The input or output may never be
serialized, but the size of documents it can handle are limited by the size
of the memory available.
More specialized memory handling approaches are possible, like building
the input tree from a serialization progressively as it is consumed,
factoring repetitive patterns, or even on-the-fly generation of the output as
the input is parsed but it is possible only for a limited subset of the
stylesheets. In general the implementation of libxslt follows the following
pattern:
- KISS (keep it simple stupid)
- when there is a clear bottleneck optimize on top of this simple
framework and refine only as much as is needed to reach the expected
result
The result is not that bad, clearly one can do a better job but more
specialized too. Most optimization like building the tree on-demand would
need serious changes to the libxml XPath framework. An easy step would be to
serialize the output directly (or call a set of SAX-like output handler to
keep this a flexible interface) and hence avoid the memory consumption of the
result.
DOM-like trees, as used and generated by libxml and libxslt, are
relatively complex. Most node types follow the given structure except a few
variations depending on the node type:
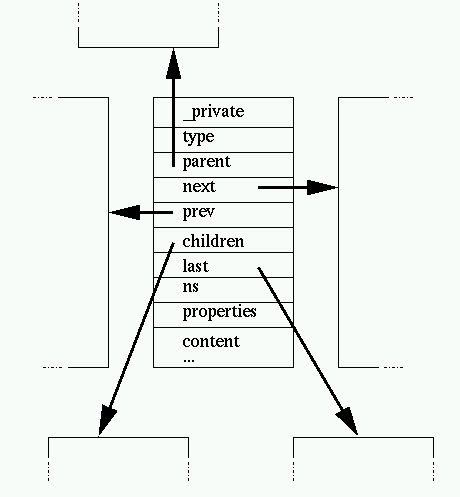
Nodes carry a name and the node type
indicates the kind of node it represents, the most common ones are:
- document nodes
- element nodes
- text nodes
For the XSLT processing, entity nodes should not be generated (i.e. they
should be replaced by their content). Most nodes also contains the following
"navigation" information:
- the containing document
- the parent node
- the first children node
- the last children node
- the previous sibling
- the following sibling (next)
Elements nodes carries the list of attributes in the properties, an
attribute itself holds the navigation pointers and the children list (the
attribute value is not represented as a simple string to allow usage of
entities references).
The ns points to the namespace declaration for the
namespace associated to the node, nsDef is the linked list
of namespace declaration present on element nodes.
Most nodes also carry an _private pointer which can be
used by the application to hold specific data on this node.
There are a few steps which are clearly decoupled at the interface
level:
- parse the stylesheet and generate a DOM tree
- take the stylesheet tree and build a compiled version of it (the
compilation phase)
- take the input and generate a DOM tree
- process the stylesheet against the input tree and generate an output
tree
- serialize the output tree
A few things should be noted here:
- the steps 1/ 3/ and 5/ are optional: the DOM representing the
stylesheet and input can be created by other means, not just by parsing
serialized XML documents, and similarly the result tree DOM can be
made available to other processeswithout being serialized.
- the stylesheet obtained at 2/ can be reused by multiple processing 4/
(and this should also work in threaded programs)
- the tree provided in 2/ should never be freed using xmlFreeDoc, but by
freeing the stylesheet.
- the input tree created in step 3/ is not modified except the
_private field which may be used for labelling keys if used by the
stylesheet. It's not modified at all in step 4/ to allow parallel
processing using a shared precompiled stylesheet.
This is the second step described. It takes a stylesheet tree, and
"compiles" it. This associates to each node a structure stored in the
_private field and containing information computed in the stylesheet:
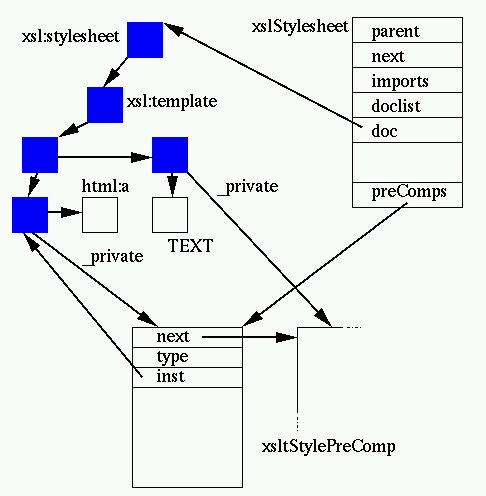
One xsltStylesheet structure is generated per document parsed for the
stylesheet. XSLT documents allow includes and imports of other documents,
imports are stored in the imports list (hence keeping the
tree hierarchy of includes which is very important for a proper XSLT
processing model) and includes are stored in the doclist
list. An imported stylesheet has a parent link to allow browsing of the
tree.
The DOM tree associated to the document is stored in doc.
It is preprocessed to remove ignorable empty nodes and all the nodes in the
XSLT namespace are subject to precomputing. This usually consist of
extracting all the context information from the context tree (attributes,
namespaces, XPath expressions), and storing them in an xsltStylePreComp
structure associated to the _private field of the node.
A couple of notable exceptions to this are XSLT template nodes (more on
this later) and attribute value templates. If they are actually templates,
the value cannot be computed at compilation time. (Some preprocessing could
be done like isolation and preparsing of the XPath subexpressions but it's
not done, yet.)
The xsltStylePreComp structure also allows storing of the precompiled form
of an XPath expression that can be associated to an XSLT element (more on
this later).
A proper handling of templates lookup is one of the keys of fast XSLT
processing. (Given a node in the source document this is the process of
finding which templates should be applied to this node.) Libxslt follows the
hint suggested in the 5.2
Patterns section of the XSLT Recommendation, i.e. it doesn't evaluate it
as an XPath expression but tokenizes it and compiles it as a set of rules to
be evaluated on a candidate node. There usually is an indication of the node
name in the last step of this evaluation and this is used as a key check for
the match. As a result libxslt builds a relatively more complex set of
structures for the templates:
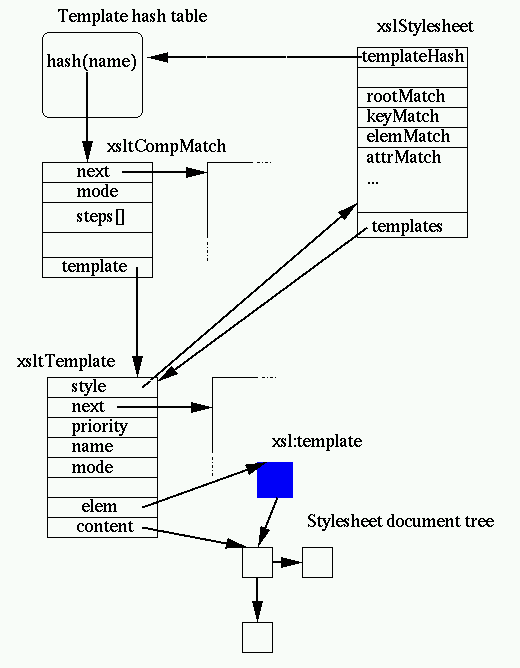
Let's describe a bit more closely what is built. First the xsltStylesheet
structure holds a pointer to the template hash table. All the XSLT patterns
compiled in this stylesheet are indexed by the value of the the target
element (or attribute, pi ...) name, so when a element or an attribute "foo"
needs to be processed the lookup is done using the name as a key.
Each of the patterns is compiled into an xsltCompMatch
(i.e. an ''XSLT compiled match') structure. It holds
the set of rules based on the tokenization of the pattern stored in reverse
order (matching is easier this way).
The xsltCompMatch are then stored in the hash table, the clash list is
itself sorted by priority of the template to implement "naturally" the XSLT
priority rules.
Associated to the compiled pattern is the xsltTemplate itself containing
the information required for the processing of the pattern including, of
course, a pointer to the list of elements used for building the pattern
result.
Last but not least a number of patterns do not fit in the hash table
because they are not associated to a name, this is the case for patterns
applying to the root, any element, any attributes, text nodes, pi nodes, keys
etc. Those are stored independently in the stylesheet structure as separate
linked lists of xsltCompMatch.
The processing is defined by the XSLT specification (the basis of the
algorithm is explained in the Introduction
section). Basically it works by taking the root of the input document
as the cureent node and applying the following algorithm:
- Finding the template applying to current node.
This is a lookup in the template hash table, walking the hash list until
the node satisfies all the steps of the pattern, then checking the
appropriate global template(s) (i.e. templates applying to a node type)
to see if there isn't a higher priority rule to apply
- If there is no template, apply the default rule (recurse on the
children as the current node)
- else walk the content list of the selected templates, for each of them:
- if the node is in the XSLT namespace then the node has a _private
field pointing to the preprocessed values, jump to the specific
code
- if the node is in an extension namespace, look up the associated
behavior
- otherwise copy the node.
The closure is usually done through the XSLT
apply-templatesconstruct, which invokes this process
recursively starting at step 1, to find the appropriate template
for the nodes selected by the 'select' attribute of the apply-templates
instruction (default: the children of the node currently being
processed)
Note that large parts of the input tree may not be processed by a given
stylesheet and that conversely some may be processed multiple times.
(This often is the case when a Table of Contents is built).
The module transform.c is the one implementing most of this
logic. xsltApplyStylesheet() is the entry point, it
allocates an xsltTransformContext containing the following:
- a pointer to the stylesheet being processed
- a stack of templates
- a stack of variables and parameters
- an XPath context
- the template mode
- current document
- current input node
- current selected node list
- the current insertion points in the output document
- a couple of hash tables for extension elements and functions
Then a new document gets allocated (HTML or XML depending on the type of
output), the user parameters and global variables and parameters are
evaluated. Then xsltProcessOneNode() which implements the
1-2-3 algorithm is called on the docuemnt node of the input. Step 1/ is
implemented by calling xsltGetTemplate(), step 2/ is
implemented by xsltDefaultProcessOneNode() and step 3/ is
implemented by xsltApplyOneTemplate().
The XPath support is actually implemented in the libxml module (where it
is reused by the XPointer implementation). XPath is a relatively classic
expression language. The only uncommon feature is that it is working on XML
trees and hence has specific syntax and types to handle them.
XPath expressions are compiled using xmlXPathCompile().
It will take an expression string in input and generate a structure
containing the parsed expression tree, for example the expression:
/doc/chapter[title='Introduction']
will be compiled as
Compiled Expression : 10 elements
SORT
COLLECT 'child' 'name' 'node' chapter
COLLECT 'child' 'name' 'node' doc
ROOT
PREDICATE
SORT
EQUAL =
COLLECT 'child' 'name' 'node' title
NODE
ELEM Object is a string : Introduction
COLLECT 'child' 'name' 'node' title
NODE
This can be tested using the testXPath command (in the
libxml codebase) using the --tree option.
Again, the KISS approach is used. No optimization is done. This could be
an interesting thing to add. Michael
Kay describes a lot of possible and interesting optimizations done in
Saxon which would be possible at this level. I'm unsure they would provide
much gain since the expressions tends to be relatively simple in general and
stylesheets are still hand generated. Optimizations at the interpretation
sounds likely to be more efficient.
The interpreter is implemented by xmlXPathCompiledEval()
which is the front-end to xmlXPathCompOpEval() the function
implementing the evaluation of the expression tree. This evaluation follows
the KISS approach again. It's recursive and calls
xmlXPathNodeCollectAndTest() to collect a set of nodes when
evaluating a COLLECT node.
An evaluation is done within the framework of an XPath context stored in
an xmlXPathContext structure, in the framework of a
transformation the context is maintained within the XSLT context. Its content
follows the requirements from the XPath specification:
- the current document
- the current node
- a hash table of defined variables (but not used by XSLT,
which uses its own stack frame for variables, described below)
- a hash table of defined functions
- the proximity position (the place of the node in the current node
list)
- the context size (the size of the current node list)
- the array of namespace declarations in scope (there also is a namespace
hash table but it is not used in the XSLT transformation).
For the purpose of XSLT an extra pointer has been added
allowing to retrieve the XSLT transformation context. When an XPath
evaluation is about to be performed, an XPath parser context is allocated
containing an XPath object stack (this is actually an XPath evaluation
context, this is a relic of the time where there was no separate parsing and
evaluation phase in the XPath implementation). Here is an overview of the set
of contexts associated to an XPath evaluation within an XSLT
transformation:
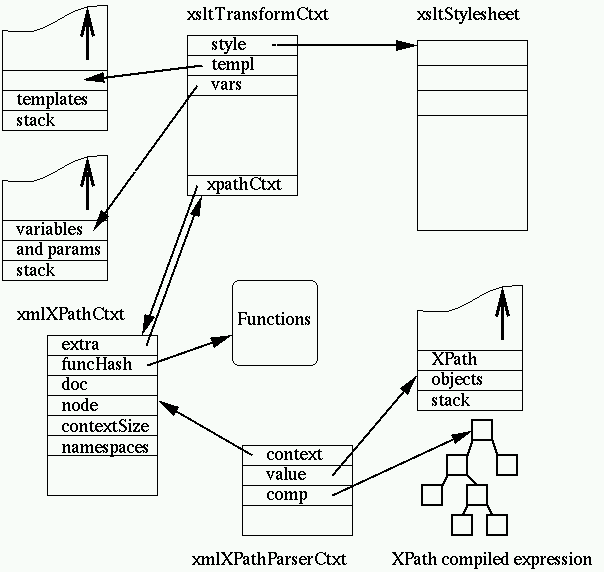
Clearly this is a bit too complex and confusing and should be refactored
at the next set of binary incompatible releases of libxml. For example the
xmlXPathCtxt has a lot of unused parts and should probably be merged with
xmlXPathParserCtxt.
An XPath expression manipulates XPath objects. XPath defines the default
types boolean, numbers, strings and node sets. XSLT adds the result tree
fragment type which is basically an unmodifiable node set.
Implementation-wise, libxml follows again a KISS approach, the
xmlXPathObject is a structure containing a type description and the various
possibilities. (Using an enum could have gained some bytes.) In the case of
node sets (or result tree fragments), it points to a separate xmlNodeSet
object which contains the list of pointers to the document nodes:
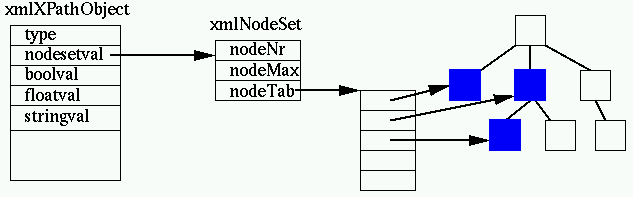
The XPath API (and
its 'internal'
part) includes a number of functions to create, copy, compare, convert or
free XPath objects.
All the XPath functions available to the interpreter are registered in the
function hash table linked from the XPath context. They all share the same
signature:
void xmlXPathFunc (xmlXPathParserContextPtr ctxt, int nargs);
The first argument is the XPath interpretation context, holding the
interpretation stack. The second argument defines the number of objects
passed on the stack for the function to consume (last argument is on top of
the stack).
Basically an XPath function does the following:
- check
nargs for proper handling of errors or functions
with variable numbers of parameters
- pop the parameters from the stack using
obj =
valuePop(ctxt);
- do the function specific computation
- push the result parameter on the stack using
valuePush(ctxt,
res);
- free up the input parameters with
xmlXPathFreeObject(obj);
- return
Sometime the work can be done directly by modifying in-situ the top object
on the stack ctxt->value.
Not to be confused with XPath object stack, this stack holds the XSLT
variables and parameters as they are defined through the recursive calls of
call-template, apply-templates and default templates. This is used to define
the scope of variables being called.
This part seems to be one needing most work , first it is
done in a very inefficient way since the location of the variables and
parameters within the stylesheet tree is still done at run time (it really
should be done statically at compile time), and I am still unsure that my
understanding of the template variables and parameter scope is actually
right.
This part of the documentation is still to be written once this part of
the code will be stable. TODO
There is a separate document explaining how the
extension support works.
Michael Kay wrote a
really interesting article on Saxon internals and the work he did on
performance issues. I wish I had read it before starting libxslt design (I
would probably have avoided a few mistakes and progressed faster). A lot of
the ideas in his papers should be implemented or at least tried in
libxslt.
The libxml documentation, especially the I/O interfaces and the memory management.
redesign the XSLT stack frame handling. Far too much work is done at
execution time. Similarly for the attribute value templates handling, at
least the embedded subexpressions ought to be precompiled.
Allow output to be saved to a SAX like output (this notion of SAX like API
for output should be added directly to libxml).
Implement and test some of the optimization explained by Michael Kay
especially:
- static slot allocation on the stack frame
- specific boolean interpretation of an XPath expression
- some of the sorting optimization
- Lazy evaluation of location path. (this may require more changes but
sounds really interesting. XT does this too.)
- Optimization of an expression tree (This could be done as a completely
independent module.)
Error reporting, there is a lot of case where the XSLT specification
specify that a given construct is an error are not checked adequately by
libxslt. Basically one should do a complete pass on the XSLT spec again and
add all tests to the stylesheet compilation. Using the DTD provided in the
appendix and making direct checks using the libxml validation API sounds a
good idea too (though one should take care of not raising errors for
elements/attributes in different namespaces).
Double check all the places where the stylesheet compiled form might be
modified at run time (extra removal of blanks nodes, hint on the
xsltCompMatch).
Thanks to Michael Sperberg-McQueen for
various fixes and clarifications on this document!
Table of content
This document describes the work needed to write extensions to the
standard XSLT library for use with libxslt, the XSLT C library developed for the GNOME project.
Before starting reading this document it is highly recommended to get
familiar with the libxslt internals.
Note: this documentation is by definition incomplete and I am not good at
spelling, grammar, so patches and suggestions are really welcome.
The XSLT specification provides
two ways to extend an XSLT engine:
In both cases the extensions need to be associated to a new namespace,
i.e. an URI used as the name for the extension's namespace (there is no need
to have a resource there for this to work).
libxslt provides a few extensions itself, either in the libxslt namespace
"http://xmlsoft.org/XSLT/namespace" or in namespaces for other well known
extensions provided by other XSLT processors like Saxon, Xalan or XT.
Since extensions are bound to a namespace name, usually sets of extensions
coming from a given source are using the same namespace name defining in
practice a group of extensions providing elements, functions or both. From
the libxslt point of view those are considered as an "extension module", and
most of the APIs work at a module point of view.
Registration of new functions or elements are bound to the activation of
the module. This is currently done by declaring the namespace as an extension
by using the attribute extension-element-prefixes on the
xsl:stylesheet
element.
An extension module is defined by 3 objects:
- the namespace name associated
- an initialization function
- a shutdown function
Currently a libxslt module has to be compiled within the application using
libxslt. There is no code to load dynamically shared libraries associated to
a namespace (this may be added but is likely to become a portability
nightmare).
The current way to register a module is to link the code implementing it
with the application and to call a registration function:
int xsltRegisterExtModule(const xmlChar *URI,
xsltExtInitFunction initFunc,
xsltExtShutdownFunction shutdownFunc);
The associated header is read by:
#include<libxslt/extensions.h>
which also defines the type for the initialization and shutdown
functions
Once the module URI has been registered and if the XSLT processor detects
that a given stylesheet needs the functionalities of an extended module, this
one is initialized.
The xsltExtInitFunction type defines the interface for an initialization
function:
/**
* xsltExtInitFunction:
* @ctxt: an XSLT transformation context
* @URI: the namespace URI for the extension
*
* A function called at initialization time of an XSLT
* extension module
*
* Returns a pointer to the module specific data for this
* transformation
*/
typedef void *(*xsltExtInitFunction)(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
const xmlChar *URI);
There are 3 things to notice:
- The function gets passed the namespace name URI as an argument. This
allows a single function to provide the initialization for multiple
logical modules.
- It also gets passed a transformation context. The initialization is
done at run time before any processing occurs on the stylesheet but it
will be invoked separately each time for each transformation.
- It returns a pointer. This can be used to store module specific
information which can be retrieved later when a function or an element
from the extension is used. An obvious example is a connection to a
database which should be kept and reused along with the transformation.
NULL is a perfectly valid return; there is no way to indicate a failure
at this level
What this function is expected to do is:
- prepare the context for this module (like opening the database
connection)
- register the extensions specific to this module
There is a single call to do this registration:
int xsltRegisterExtFunction(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
const xmlChar *name,
const xmlChar *URI,
xmlXPathEvalFunc function);
The registration is bound to a single transformation instance referred by
ctxt, name is the UTF8 encoded name for the NCName of the function, and URI
is the namespace name for the extension (no checking is done, a module could
register functions or elements from a different namespace, but it is not
recommended).
The implementation of the function must have the signature of a libxml
XPath function:
/**
* xmlXPathEvalFunc:
* @ctxt: an XPath parser context
* @nargs: the number of arguments passed to the function
*
* an XPath evaluation function, the parameters are on the
* XPath context stack
*/
typedef void (*xmlXPathEvalFunc)(xmlXPathParserContextPtr ctxt,
int nargs);
The context passed to an XPath function is not an XSLT context but an XPath context. However it is possible to
find one from the other:
The first thing an extension function may want to do is to check the
arguments passed on the stack, the nargs parameter will tell how
many of them were provided on the XPath expression. The macro valuePop will
extract them from the XPath stack:
#include <libxml/xpath.h>
#include <libxml/xpathInternals.h>
xmlXPathObjectPtr obj = valuePop(ctxt);
Note that ctxt is the XPath context not the XSLT one. It is
then possible to examine the content of the value. Check the description of XPath objects if
necessary. The following is a common sequence checking whether the argument
passed is a string and converting it using the built-in XPath
string() function if this is not the case:
if (obj->type != XPATH_STRING) {
valuePush(ctxt, obj);
xmlXPathStringFunction(ctxt, 1);
obj = valuePop(ctxt);
}
Most common XPath functions are available directly at the C level and are
exported either in <libxml/xpath.h> or in
<libxml/xpathInternals.h>.
The extension function may also need to retrieve the data associated to
this module instance (the database connection in the previous example) this
can be done using the xsltGetExtData:
void * xsltGetExtData(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
const xmlChar *URI);
Again the URI to be provided is the one which was used when registering
the module.
Once the function finishes, don't forget to:
- push the return value on the stack using
valuePush(ctxt,
obj)
- deallocate the parameters passed to the function using
xmlXPathFreeObject(obj)
The module libxslt/functions.c contains the sources of the XSLT built-in
functions, including document(), key(), generate-id(), etc. as well as a full
example module at the end. Here is the test function implementation for the
libxslt:test function:
/**
* xsltExtFunctionTest:
* @ctxt: the XPath Parser context
* @nargs: the number of arguments
*
* function libxslt:test() for testing the extensions support.
*/
static void
xsltExtFunctionTest(xmlXPathParserContextPtr ctxt, int nargs)
{
xsltTransformContextPtr tctxt;
void *data;
tctxt = xsltXPathGetTransformContext(ctxt);
if (tctxt == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtFunctionTest: failed to get the transformation context\n");
return;
}
data = xsltGetExtData(tctxt, (const xmlChar *) XSLT_DEFAULT_URL);
if (data == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtFunctionTest: failed to get module data\n");
return;
}
#ifdef WITH_XSLT_DEBUG_FUNCTION
xsltGenericDebug(xsltGenericDebugContext,
"libxslt:test() called with %d args\n", nargs);
#endif
}
There is a single call to do this registration:
int xsltRegisterExtElement(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
const xmlChar *name,
const xmlChar *URI,
xsltTransformFunction function);
It is similar to the mechanism used to register an extension function,
except that the signature of an extension element implementation is
different.
The registration is bound to a single transformation instance referred to
by ctxt, name is the UTF8 encoded name for the NCName of the element, and URI
is the namespace name for the extension (no checking is done, a module could
register elements for a different namespace, but it is not recommended).
The implementation of the element must have the signature of an XSLT
transformation function:
/**
* xsltTransformFunction:
* @ctxt: the XSLT transformation context
* @node: the input node
* @inst: the stylesheet node
* @comp: the compiled information from the stylesheet
*
* signature of the function associated to elements part of the
* stylesheet language like xsl:if or xsl:apply-templates.
*/
typedef void (*xsltTransformFunction)
(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
xmlNodePtr node,
xmlNodePtr inst,
xsltStylePreCompPtr comp);
The first argument is the XSLT transformation context. The second and
third arguments are xmlNodePtr i.e. internal memory representation of XML nodes. They are
respectively node from the the input document being transformed
by the stylesheet and inst the extension element in the
stylesheet. The last argument is comp a pointer to a precompiled
representation of inst but usually for an extension function
this value is NULL by default (it could be added and associated
to the instruction in inst->_private).
The same functions are available from a function implementing an extension
element as in an extension function, including
xsltGetExtData().
The goal of an extension element being usually to enrich the generated
output, it is expected that they will grow the currently generated output
tree. This can be done by grabbing ctxt->insert which is the current
libxml node being generated (Note this can also be the intermediate value
tree being built for example to initialize a variable, the processing should
be similar). The functions for libxml tree manipulation from <libxml/tree.h> can
be employed to extend or modify the tree, but it is required to preserve the
insertion node and its ancestors since there are existing pointers to those
elements still in use in the XSLT template execution stack.
The module libxslt/transform.c contains the sources of the XSLT built-in
elements, including xsl:element, xsl:attribute, xsl:if, etc. There is a small
but full example in functions.c providing the implementation for the
libxslt:test element, it will output a comment in the result tree:
/**
* xsltExtElementTest:
* @ctxt: an XSLT processing context
* @node: The current node
* @inst: the instruction in the stylesheet
* @comp: precomputed information
*
* Process a libxslt:test node
*/
static void
xsltExtElementTest(xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt, xmlNodePtr node,
xmlNodePtr inst,
xsltStylePreCompPtr comp)
{
xmlNodePtr comment;
if (ctxt == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtElementTest: no transformation context\n");
return;
}
if (node == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtElementTest: no current node\n");
return;
}
if (inst == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtElementTest: no instruction\n");
return;
}
if (ctxt->insert == NULL) {
xsltGenericError(xsltGenericErrorContext,
"xsltExtElementTest: no insertion point\n");
return;
}
comment =
xmlNewComment((const xmlChar *)
"libxslt:test element test worked");
xmlAddChild(ctxt->insert, comment);
}
When the XSLT processor ends a transformation, the shutdown function (if
it exists) for each of the modules initialized is called. The
xsltExtShutdownFunction type defines the interface for a shutdown
function:
/**
* xsltExtShutdownFunction:
* @ctxt: an XSLT transformation context
* @URI: the namespace URI for the extension
* @data: the data associated to this module
*
* A function called at shutdown time of an XSLT extension module
*/
typedef void (*xsltExtShutdownFunction) (xsltTransformContextPtr ctxt,
const xmlChar *URI,
void *data);
This is really similar to a module initialization function except a third
argument is passed, it's the value that was returned by the initialization
function. This allows the routine to deallocate resources from the module for
example close the connection to the database to keep the same example.
Well, some of the pieces missing:
- a way to load shared libraries to instantiate new modules
- a better detection of extension functions usage and their registration
without having to use the extension prefix which ought to be reserved to
element extensions.
- more examples
- implementations of the EXSLT common
extension libraries, Thomas Broyer nearly finished implementing them.
Daniel Veillard







